Since their invention 70-plus years ago, barcodes have transformed the business landscape by enabling companies to become more efficient in their daily operations and this technology has proven critical to the success of many businesses – yet few companies think about ways to go about maximizing this remarkable technology.
- What is a barcode
- How does it work?
- What is a barcode scanner and how do they work?
- Benefits of using a barcode scanner
- How Datalogic barcode scanners can help
WHAT IS A BARCODE
At a basic level, barcodes are a machine-readable representation of data that are usually printed on products. They are used for tracking inventory and for price look-ups at the point of sale. In most cases, barcodes are linear, consisting of a series of vertical lines of varying widths and the lines are read by a barcode scanner, which converts the pattern of lines into a digital signal which can be read by a computer. Barcodes today are found literally everywhere from retail stores to warehouses and hospitals. In each case, they encode important details which help to identify a product or person.
HOW DOES IT WORK?
Given the increasing importance of barcodes for most businesses today, how do they work then? In a nutshell, barcodes are made up of a series of black and white bars of varying widths. The widths of the bars are encoded with binary data representing the numbers 0 or 1 while the sequence of the bars represents a number between 0 and 9. This data can be decoded by a barcode scanner, which reads the barcode and translates it into a numerical value. The computer with all the information connected to a barcode scanner will be able to read the unique combination of bars and spaces and may add, multiply or divide those numbers to identify the correct product before displaying it on the screen.
BARCODE COMPONENTS
Barcodes must be designed in a specific and uniform way such that a barcode scanner can read them and relay the encoded data back to the computer. There are four main components to a barcode: the quiet zone, the start character, the data characters, and the stop character.
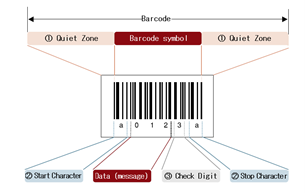
Quiet zone: The quiet zone is a blank area on either side of the barcode that ensures the scanner can properly read the code.
Start character/Stop character: The start character is a unique pattern that tells the scanner that a barcode is about to be read. And finally, the stop character is another unique pattern that tells the scanner that the barcode has been completely read
Data (message): The data contains the actual information that is being encoded in the barcode.
Check digit: The check digit is a digit to check for accuracy of the encoded barcode data and flags any potential errors.
TYPES OF BARCODES
There are several different types of barcodes in use today, but they can be grouped into 2 main categories, 1D and 2D barcodes.

1D barcodes: The most common type of barcodes used on products and inventory tags. The most popular 1D barcode is the UPC (Universal Product Code), which is used in North America. They are created by printing a pattern of bars and spaces that represent numbers, letters, or other symbols tied to set of information in a database containing details such as product name, type, size and colour. 1D barcodes are used in a variety of applications, such as inventory control, product labelling, and document management.

2D barcodes: 2D barcodes are becoming increasingly popular, as they can store more information than 1D barcodes. They are essentially two-dimensional versions of the familiar linear barcodes that have been used for decades and able to store more information such as quantity, images and website URLs. 2D barcodes are often used on loyalty cards, ID cards, and in mobile marketing applications. One good example is QR codes which are two-dimensional barcodes that can be scanned by smartphones and other devices with camera scanners. QR codes are often used to encode links to websites, videos, and other online content.
WHAT IS A BARCODE SCANNER AND HOW DO THEY WORK?
It is redundant to have barcodes if we didn’t have the technology to read them and that is where barcode scanners come in. Barcode scanners can be in the form of handheld or fixed mount devices that read barcodes and convert them into digital data.
TYPES OF BARCODE SCANNERS
Barcode scanners are typically made up of three separate components: an illumination system, a sensor, and a decoder. In general, a barcode scanner “read” the black and white elements of a barcode by illuminating the code with a red light, which is then converted into matching text. Specifically, the sensor detects the reflected light from the illumination system (the red light) and generates an analog signal that is sent to the decoder. The decoder then analyses the signal provided by the sensor, validates against the check digit before converting it into text. The captured text is then delivered by the scanner to the computer software database which holds the product details.
As noted earlier, barcode scanners can be in the form of handheld or fixed mount devices, below are some common examples.
Laser scanners: A laser barcode scanner uses laser beams as a light source to illuminate the barcode so it can be read. The laser shoots a beam of light back and forth across the barcode and the photodiode in the laser scanner then measures the reflected light from the barcode, create an analog signal before converting it into a digital signal. Such scanners offer accuracy and high precision in barcode reading while reading from a greater distance.

2D area imagers: 2D area imagers works by using modern camera technology to capture the code before decoding it with an algorithm to relay the information back to the computer. 2D area imagers such as Datalogic Gryphon™ 4500 are great for scanning smaller barcodes.

Omni directional scanners: Omni directional scanning such as Datalogic Magellan™ 1500i relies on a complex and interwoven series of lasers creating a mixed-grid pattern. They are laser scanners, but the omni-directional functionality enables them to decode 2D barcodes as well as 1D barcodes.
Barcodes scanners have taken off in a big way as it offers an efficient and fast return on investment. Lets go through some of the key benefits associated with it:
Easy to implement: Barcode scanners can be set up quickly with minimal disruption to existing operations while employees can operate the scanners within a short time frame with little training. For most part, it is a self-explanatory device.
Improves productivity: Each time a barcode is scan by a worker, the inventory and sales numbers sitting inside the company’s enterprise resource planning (ERP) gets updated in real time. This allows access to updated information in a few seconds without having to rummage through old files and lost papers.
Reduces error: A recent study found that up to 50% of data errors in the warehouse are due to human error. Regardless of how careful your workers are, every once in a while, there’s a ‘fat finger’ error or someone might mistake 1 for l, or enter the wrong product description. This can affect the inventory management process and cause trouble for both consumers and retailers. Bar code scanners eliminate these human errors
HOW DATALOGIC BARCODE SCANNERS CAN HELP
Many industries today rely on barcode and barcode scanners for their daily operations. Datalogic has been a trusted barcode scanner manufacturer for over 50 years and offers a wide range of products to suit businesses of all sizes. Today, Datalogic barcode scanners are used in more than 100 countries and in a variety of applications to improve efficiency and accuracy.









